Sunshine Factory, Co., Ltd. > Applications > ZrP for PolymerZrP for Polymer
Great Potential for High Density Polyethylene Innovations
Abstract
The addition of fillers enhances mechanical, thermal and barrier properties of the composites.
The use of layered zirconium phosphate (ZrP), an inorganic and synthetic filler, in the formation of a nanocomposite, results in a material with higher aspect ratio, purity and surface energy advantages in relation to MMT.
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a semicrystalline polymer with many advantages – low density, strong tenacity, high resistance to impact, abrasion and corrosion. Additionally, inertia to the majority of chemicals, low toxicity and long lifetime, contribute to large industrial applications.
The aim of this work was to investigate the influence of the intercalation of octadecylamine inside ZrP galleries on the HDPE characteristics.
Through thermal, crystallographic, thermo-mechanical, tensile and molecular mobility analyses, the formation of
intercalated and/or exfoliated nanocomposite was evaluated.
Through thermal, crystallographic, thermo-mechanical, tensile and molecular mobility analyses, the formation of
intercalated and/or exfoliated nanocomposite was evaluated.
Nanocomposite based on high density polyethylene (HDPE) and layered zirconium phosphate organically modified with octadecylamine (ZrPOct) was obtained through melt processing.
Modification of the layered zirconium phosphate
A certain amount of α-ZrP and a solution of octadecylamine (2:1 alcohol/water) were mixed at an amine/α-ZrP molar ratio of 1.5.
The product was centrifuged and washed successively with alcohol to remove the excess of amine. As before, the resulting solid was placed in a freezer at –80 °C for 24 hours and then submitted to lyophilization for 4 days.
The final product was labeled as ZrPOct.
The product was centrifuged and washed successively with alcohol to remove the excess of amine. As before, the resulting solid was placed in a freezer at –80 °C for 24 hours and then submitted to lyophilization for 4 days.
The final product was labeled as ZrPOct.
Preparation of nanocomposites
Results
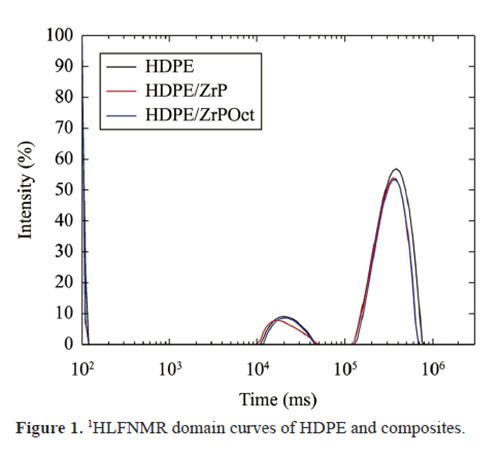
Hydrogen low field nuclear magnetic resonance
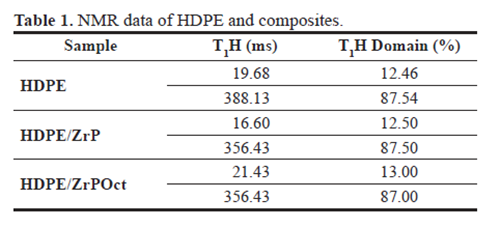
Dynamic-mechanical test
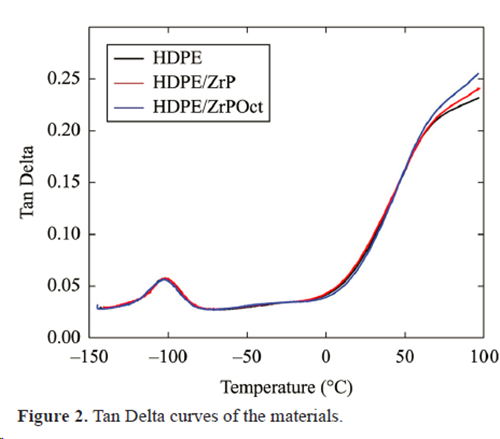

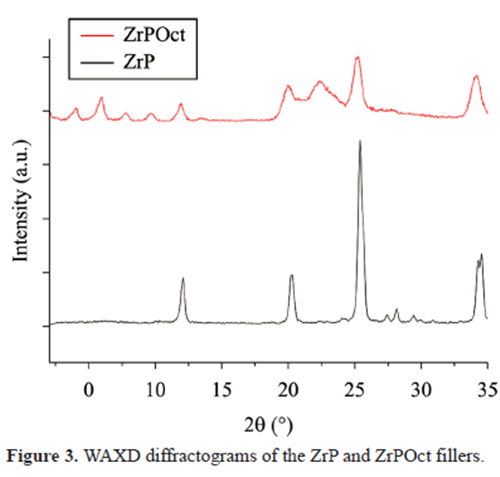
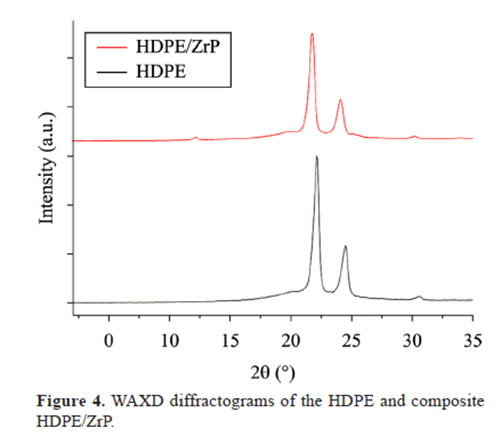
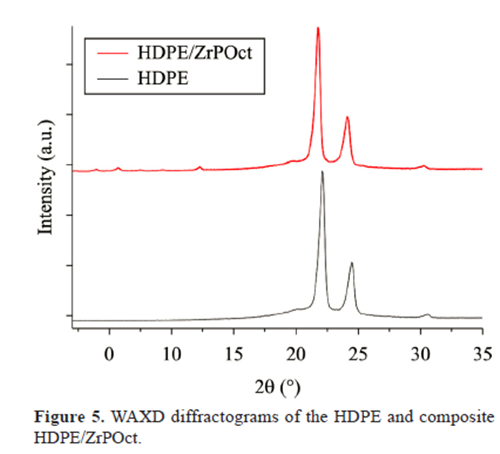
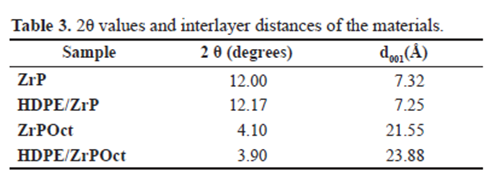
WAXD
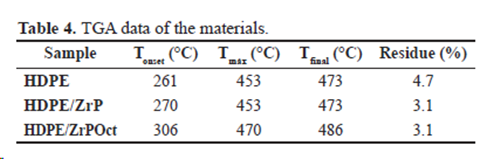
Thermogravimetry
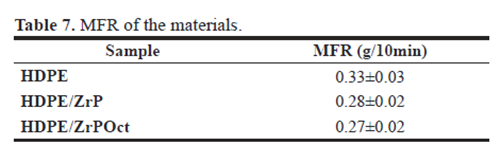
Differential scanning calorimetry
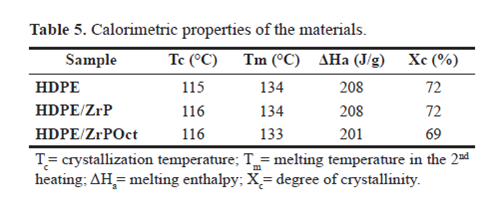
Mechanical measurements
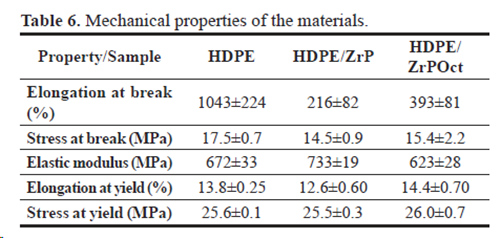
Melt flow rate
On the contrary, presence of octadecylamine as intercalation agent of ZrP allowed the increasing of its interlamellar
Nanocomposites of HDPE and layered zirconium phosphates– neat and organically modified with octadecylamine – with
a fixed phosphate percentage of 2% w/w, were processed in a counter-rotating twin-screw extruder.
The extruder was adjusted to operate at 100 rpm and temperature profile of 160 °C (input) and 170 °C, 180 °C and 190 °C (output), conditions recommended by the polymer manufacturer.
The extrudate was cooled and granulated. In order to homogenize the nanocomposite, the material was reprocessed under the
The extruder was adjusted to operate at 100 rpm and temperature profile of 160 °C (input) and 170 °C, 180 °C and 190 °C (output), conditions recommended by the polymer manufacturer.
The extrudate was cooled and granulated. In order to homogenize the nanocomposite, the material was reprocessed under the
same conditions.
In order to characterize the material, thin plates was processed in Carver press at 210 °C, with load of 5000 kg for 7 minutes.
In order to characterize the material, thin plates was processed in Carver press at 210 °C, with load of 5000 kg for 7 minutes.
Results
Hydrogen low field nuclear magnetic resonance


Dynamic-mechanical test


WAXD




Thermogravimetry

Differential scanning calorimetry

Mechanical measurements

Melt flow rate

Conclusions
Alpha-zirconium phosphate was synthesized and modified with octadecylamine in order to produce nanocomposite based
on HDPE.
According to some conventional characterization techniques of polymers (DSC, TGA, WAXD, MFR, tensile‑deformation) HDPE/ZrP behave as a microcomposite.
According to some conventional characterization techniques of polymers (DSC, TGA, WAXD, MFR, tensile‑deformation) HDPE/ZrP behave as a microcomposite.
On the contrary, presence of octadecylamine as intercalation agent of ZrP allowed the increasing of its interlamellar
spacing.
Also facilitate the entrance of the HDPE chain along the filler galleries. This produced changes in the HDPE behavior.
Decreasing of the (d001) diffraction angle, elastic modulus, degree of crystallinity besides increasing of the interlamellar spacing and thermal stability, lead to inducing that a partially and/or exfoliated nanocomposite was reached.
Also facilitate the entrance of the HDPE chain along the filler galleries. This produced changes in the HDPE behavior.
Decreasing of the (d001) diffraction angle, elastic modulus, degree of crystallinity besides increasing of the interlamellar spacing and thermal stability, lead to inducing that a partially and/or exfoliated nanocomposite was reached.

Follow WeChat


