Sunshine Factory, Co., Ltd. > ApplicationsApplications
Zirconium Phosphate ion-exchange capacity in water treatment
Water from municipal water supplies, must be purified or treated, in order to reduce the level of contaminants present in the water to levels that are acceptable for consumption, or other human use. Contaminants which may be present in municipal tap water include, for example, toxic ionic contaminants, organic compounds, microbes, mold, and/or algae.
Zirconium ion-exchange resins, and particularly, mixed bed ion-exchange resins, can provide useful sorbents for de-ionizing water and removing toxic contaminants in water. Zirconium ion-exchange sorbents are safe and non-toxic.
To achieve the above noted goals, 3 kinds of chemical, sodium zirconium phosphate (NaZrP), zirconium phosphate (AZP) and alkaline hydrous zirconium oxide (NaHZO) are employed for water purification. There are 3 experimental examples to exhibit the purification effectiveness.
Example 1
[About 500 gallons of contaminated feed water was treated using the cartridge of the present invention. The cartridge was about 5" in diameter and about 12" in height. The components of the cartridge were in the following order (as layers):
1. Particle filter pad
2. 1200 gm [H+-ZP:HZO-OH ] (55:45 wt ratio)
3. Filter paper
4. 500 gm [Na+-ZP]
5. Carbon pad
6. 500 gm activated carbon (Calgon)
7. Carbon pad
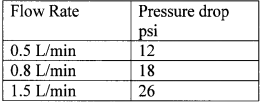
The specifications of the contaminated feed water are provided in Table 2 below. The specifications of the product (resulting) water quality are provided in Table 3 below. The water flow rate and pressure drop are provided in Table 4 below.
Table 2. Challenge test contaminated water quality
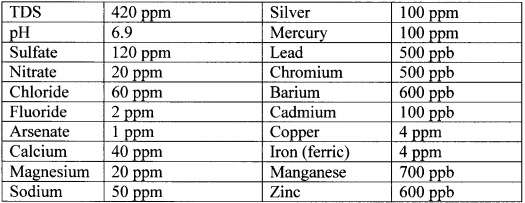
Table 3. Product water quality (500 gal life test with flow rate at 1 liter/min)
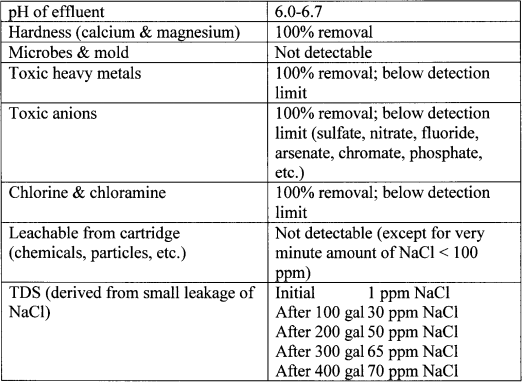
Table 4. Pressure drop of 5" diameter model
Example 2
About 100 gallons of impure water was treated at a challenge level of individual contaminant, using the same cartridge components as in Example 1. The water flow rate was 500 ml/min. The specifications of the resulting purified water are provided in Tables 5-7 below.
Table 5. Purity of product water-Cations
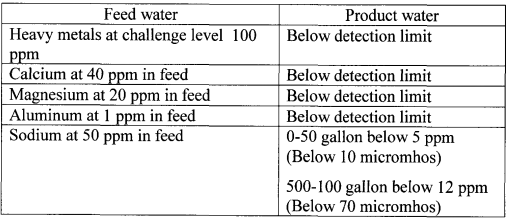
Table 6. Purity of product water- Anions
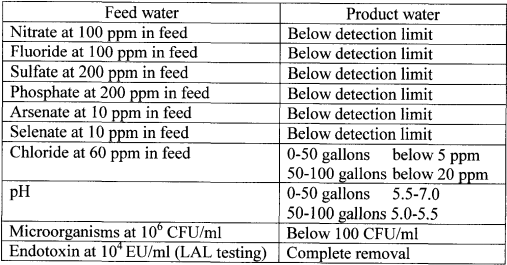
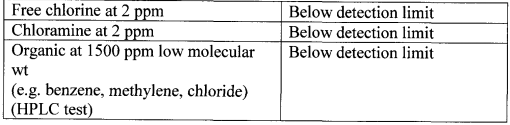
Table 7. Purity of product water-Disinfectants
Example 3
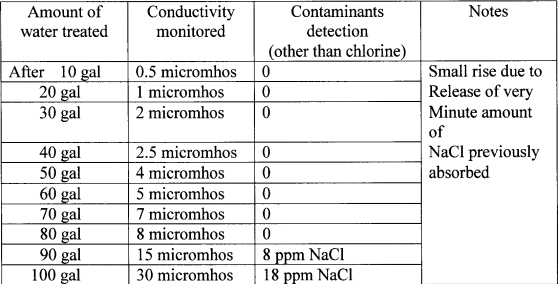
The removal efficiency of toxic chemicals from water using a cartridge having, aside from a monolayer of mixed H+-ZP:HZO-OH", no additional zirconium ion-exchange resins present. A carbon pad was below the layer and a particle filter pad was above. The cartridge was about 5" in diameter and contained about 2250 gm of H -ZP:HZO-OH- (blending ratio 1 : 1 by weight). The levels of adsorption of toxic chemicals from the contaminated water, with a flow rate of 500 ml/min, are provided in Table 8 below. The conductivity of the water during treatment is provided in Table 9 below.
Table 8. Removal of toxic chemicals
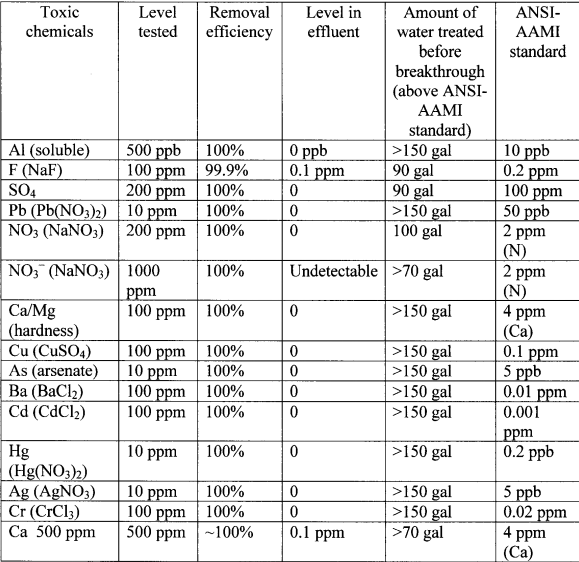
Table 9. Conductivity monitoring during treatment of municipal water
(NOTE: Conductivity of OKC tap water 130 micromhos)
Zirconium ion-exchange resins, and particularly, mixed bed ion-exchange resins, can provide useful sorbents for de-ionizing water and removing toxic contaminants in water. Zirconium ion-exchange sorbents are safe and non-toxic.
To achieve the above noted goals, 3 kinds of chemical, sodium zirconium phosphate (NaZrP), zirconium phosphate (AZP) and alkaline hydrous zirconium oxide (NaHZO) are employed for water purification. There are 3 experimental examples to exhibit the purification effectiveness.
Example 1
[About 500 gallons of contaminated feed water was treated using the cartridge of the present invention. The cartridge was about 5" in diameter and about 12" in height. The components of the cartridge were in the following order (as layers):
1. Particle filter pad
2. 1200 gm [H+-ZP:HZO-OH ] (55:45 wt ratio)
3. Filter paper
4. 500 gm [Na+-ZP]
5. Carbon pad
6. 500 gm activated carbon (Calgon)
7. Carbon pad
The specifications of the contaminated feed water are provided in Table 2 below. The specifications of the product (resulting) water quality are provided in Table 3 below. The water flow rate and pressure drop are provided in Table 4 below.
Table 2. Challenge test contaminated water quality

Table 3. Product water quality (500 gal life test with flow rate at 1 liter/min)

Table 4. Pressure drop of 5" diameter model

Example 2
About 100 gallons of impure water was treated at a challenge level of individual contaminant, using the same cartridge components as in Example 1. The water flow rate was 500 ml/min. The specifications of the resulting purified water are provided in Tables 5-7 below.
Table 5. Purity of product water-Cations

Table 6. Purity of product water- Anions

Table 7. Purity of product water-Disinfectants

Example 3
The removal efficiency of toxic chemicals from water using a cartridge having, aside from a monolayer of mixed H+-ZP:HZO-OH", no additional zirconium ion-exchange resins present. A carbon pad was below the layer and a particle filter pad was above. The cartridge was about 5" in diameter and contained about 2250 gm of H -ZP:HZO-OH- (blending ratio 1 : 1 by weight). The levels of adsorption of toxic chemicals from the contaminated water, with a flow rate of 500 ml/min, are provided in Table 8 below. The conductivity of the water during treatment is provided in Table 9 below.
Table 8. Removal of toxic chemicals

Table 9. Conductivity monitoring during treatment of municipal water
(NOTE: Conductivity of OKC tap water 130 micromhos)


Follow WeChat


