Sunshine Factory, Co., Ltd. > Applications > ZrP for CatalystZrP for Catalyst
A laminar nanocomposite constructed by self-assembly of exfoliated a-ZrP nanosheets and manganese porphyrin for use in the electrocatalytic oxidation of nitrite
Abstract
Laminar nanocomposite of α-ZrP/MnTMPyP, [5, 10, 15, 20-tetrakis (N-methylpyridinium-4-yl) porphyrinato manganese (III)], was obtained through the selfassembly of α-ZrP nanosheets and manganese porphyrin molecules, namely the exfoliation/restacking route.
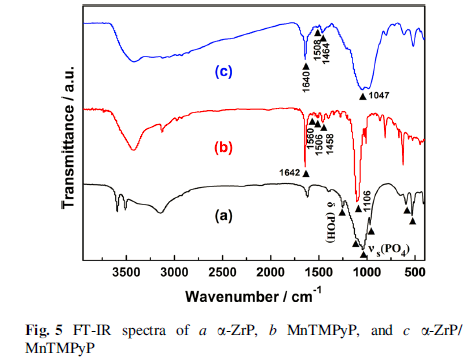
The final products were characterized by several analytic techniques such as XRD, IR, UV–Vis, and SEM. Meanwhile, the surface charge change of layered zirconium phosphate during the restacking process was monitored by a Zetasizer Nano instrument. The zeta potential value of α-ZrP colloidal dispersion is -40.1 mV, indicating that the colloidal dispersion was stable and well dispersed.
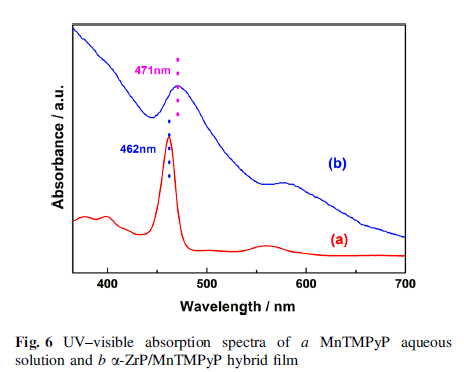
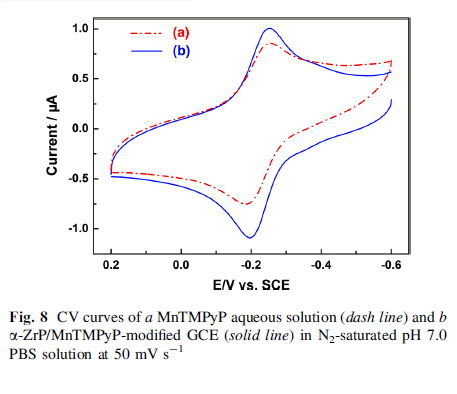
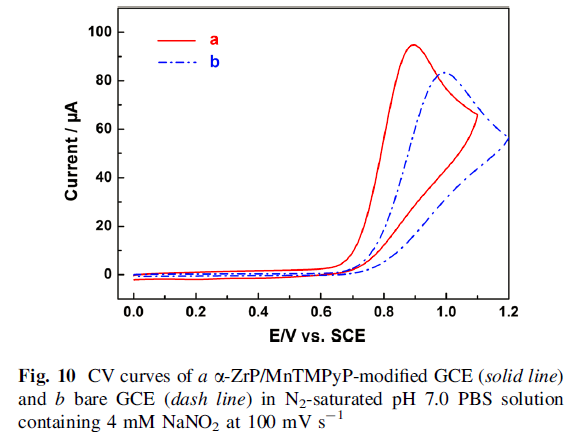
The cyclic voltammetry measurements of α -ZrP/MnTMPyP film-modified glass carbon electrode displayed a pair of well-defined oxidation/reduction peaks with redox potentials at -0.256 and -0.197 V with an increase in the peakcurrent compared to MnTMPyP aqueous solution. Furthermore, α-ZrP/MnTMPyP hybrid thin film exhibited excellent electrocatalytic activities toward oxidation of nitrite.
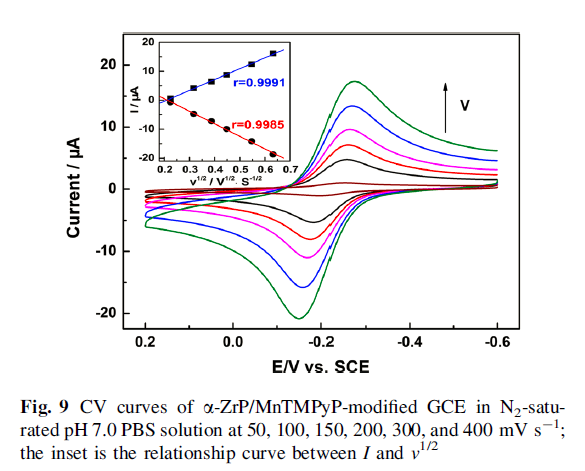
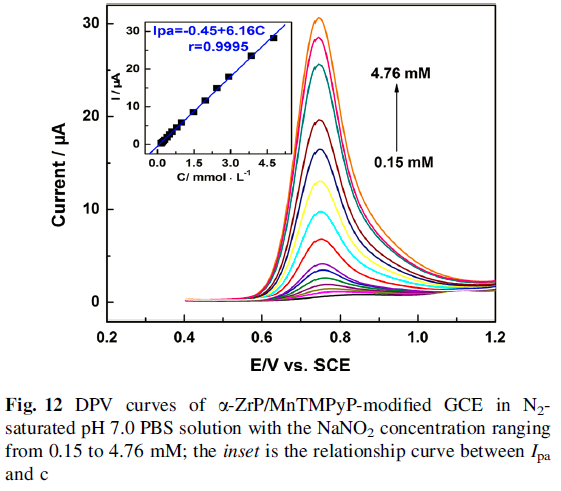
The oxidation peak current increased linearly with the square root of scan rate, suggesting that the electrocatalytic process was controlled by nitrite diffusion. Finally, a detection limit of 5.3 X 10-5 M was estimated at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3.0 with a concentration range of 1.5 X10-4 to 4.76 X10-3 M.
Introduction
α-Zr(HPO4)2·H2O (abbreviated as α-ZrP) owns several characteristics such as larger surface charge density and higher aspect ratio and ion-exchange capacity except for commonalities of layered nanomaterials. Hence, some related articles about preparation of the intercalation compounds ofα-ZrP/MB (methylene blue) , α-ZrP/porphyrin , α-ZrP/hemoglobin, and α-ZrP/insulin were reported.
In addition, α-ZrP has been modified to obtain various hybrid materials with diverse applications by replacing hydroxyl groups located on the surface of α-ZrP with organic functional groups.
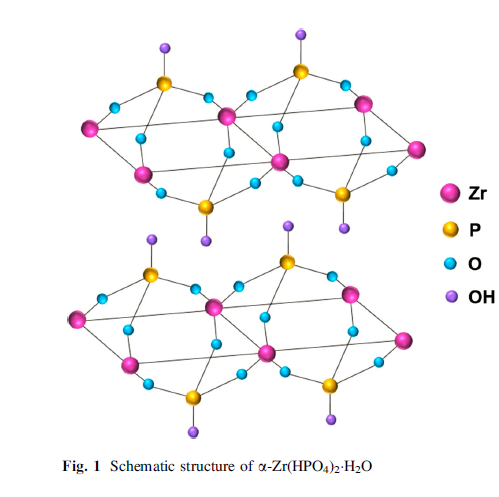
Concerning the structure of α -ZrP, three oxygen atoms belonging to one phosphate group are bonded to three different Zr atoms forming the laminate, while OH connecting to P atoms points into the interlayer region or on the surface (Fig. 1).
Experimental



Conclusions
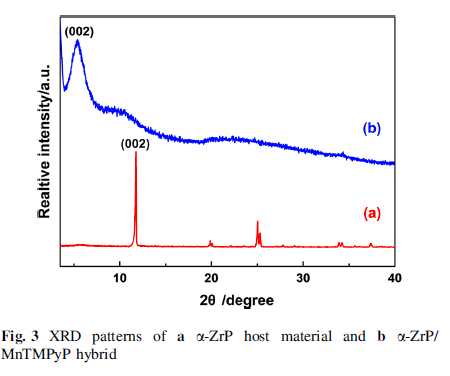
A convenient method called the exfoliation/restacking route was adopted to prepare α-ZrP/MnTMPyP laminar nanocomposite. The α -ZrP colloidal suspension obtained in the delamination process was traced by a Zetasizer Nano instrument.
In addition, the arrangement of MnTMPyP molecule in the galley of the hybrid has been proposed. The CV measurements of α-ZrP/MnTMPyP film-modified GCE indicated that the as-obtained nanocomposite has exhibited excellent electrocatalytic activities on the oxidation of nitrite in pH 7.0 PBS. A detection limit of 5.3 X 10-5 M was estimated at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3.0 indicated by DPV results.
Laminar nanocomposite of α-ZrP/MnTMPyP, [5, 10, 15, 20-tetrakis (N-methylpyridinium-4-yl) porphyrinato manganese (III)], was obtained through the selfassembly of α-ZrP nanosheets and manganese porphyrin molecules, namely the exfoliation/restacking route.
The final products were characterized by several analytic techniques such as XRD, IR, UV–Vis, and SEM. Meanwhile, the surface charge change of layered zirconium phosphate during the restacking process was monitored by a Zetasizer Nano instrument. The zeta potential value of α-ZrP colloidal dispersion is -40.1 mV, indicating that the colloidal dispersion was stable and well dispersed.
The cyclic voltammetry measurements of α -ZrP/MnTMPyP film-modified glass carbon electrode displayed a pair of well-defined oxidation/reduction peaks with redox potentials at -0.256 and -0.197 V with an increase in the peakcurrent compared to MnTMPyP aqueous solution. Furthermore, α-ZrP/MnTMPyP hybrid thin film exhibited excellent electrocatalytic activities toward oxidation of nitrite.
The oxidation peak current increased linearly with the square root of scan rate, suggesting that the electrocatalytic process was controlled by nitrite diffusion. Finally, a detection limit of 5.3 X 10-5 M was estimated at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3.0 with a concentration range of 1.5 X10-4 to 4.76 X10-3 M.
Introduction
α-Zr(HPO4)2·H2O (abbreviated as α-ZrP) owns several characteristics such as larger surface charge density and higher aspect ratio and ion-exchange capacity except for commonalities of layered nanomaterials. Hence, some related articles about preparation of the intercalation compounds ofα-ZrP/MB (methylene blue) , α-ZrP/porphyrin , α-ZrP/hemoglobin, and α-ZrP/insulin were reported.
In addition, α-ZrP has been modified to obtain various hybrid materials with diverse applications by replacing hydroxyl groups located on the surface of α-ZrP with organic functional groups.
Concerning the structure of α -ZrP, three oxygen atoms belonging to one phosphate group are bonded to three different Zr atoms forming the laminate, while OH connecting to P atoms points into the interlayer region or on the surface (Fig. 1).

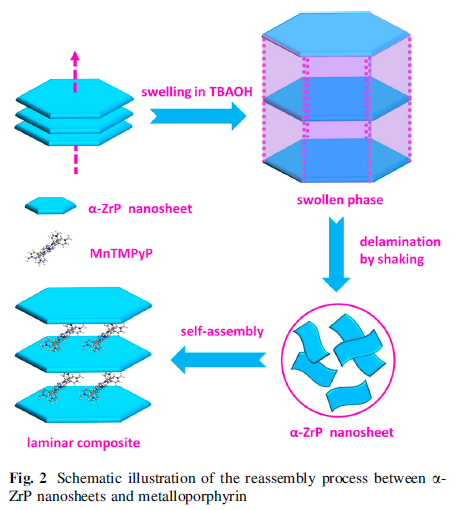
The exfoliation of a-ZrP nanosheets has also become the research focus . Therefore, it is promising to introduce metalloporphyrin into the interlayer of a-ZrP through the exfoliation/restackingmethod (Fig. 2).

Experimental










Conclusions
A convenient method called the exfoliation/restacking route was adopted to prepare α-ZrP/MnTMPyP laminar nanocomposite. The α -ZrP colloidal suspension obtained in the delamination process was traced by a Zetasizer Nano instrument.
In addition, the arrangement of MnTMPyP molecule in the galley of the hybrid has been proposed. The CV measurements of α-ZrP/MnTMPyP film-modified GCE indicated that the as-obtained nanocomposite has exhibited excellent electrocatalytic activities on the oxidation of nitrite in pH 7.0 PBS. A detection limit of 5.3 X 10-5 M was estimated at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3.0 indicated by DPV results.

Follow WeChat


