Sunshine Factory, Co., Ltd. > Applications > Lubricants, Lithium greaseLubricants, Lithium grease
The Tribological Properites with solid lubricant MoS2 , Graphite and Zirconium Phosphate additives in PEG 400 Base oil
Abstract
Introduction
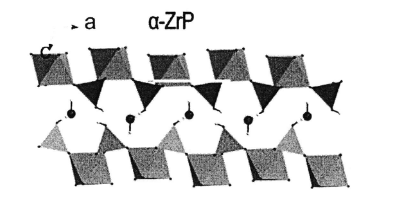
1. Layered Structure of α-ZrP
2. SEM-images of α-ZrP

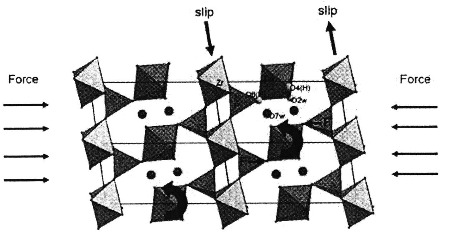
3. Scheme of the mechanism for α-ZrP
4. SEM and EDS observation of worn surface of grease with additive of α-ZrP after the test
The testing results about using Zirconium (Hydrogen) Phosphate(ZrP) in solid lubricant
The tribological properites with different additives in PEG 400 Base oil
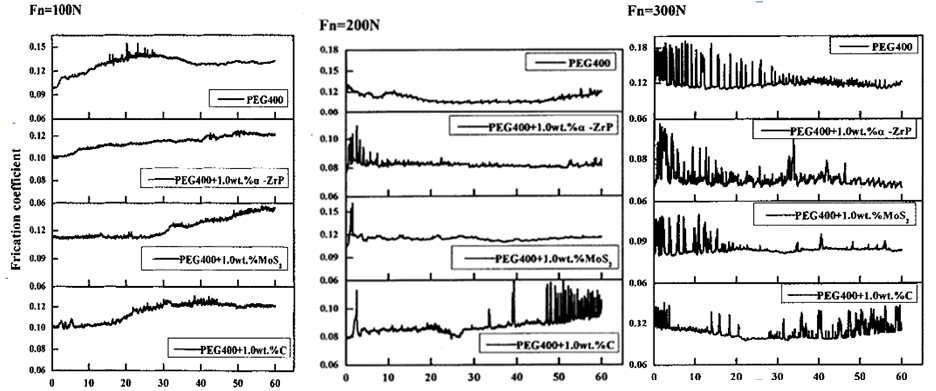
1). Dynamic friction coefficient curves for α-ZrP、MoS2 and Graphite under various applied loads in PEG 400 base oil
2). Friction coefficient for α-ZrP、 MoS2 and Graphite under various frequencies in PEG 400 base oil

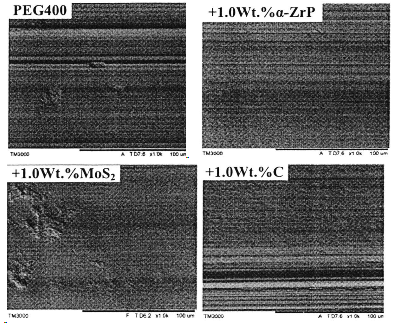
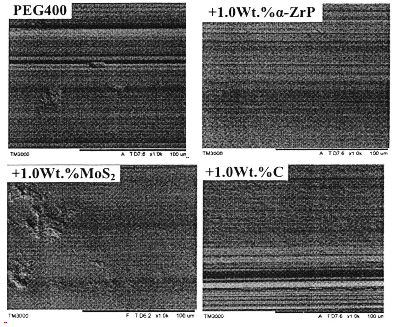
3). SEM Images of wear scars lubricated by different additives in PEG 400 base oil
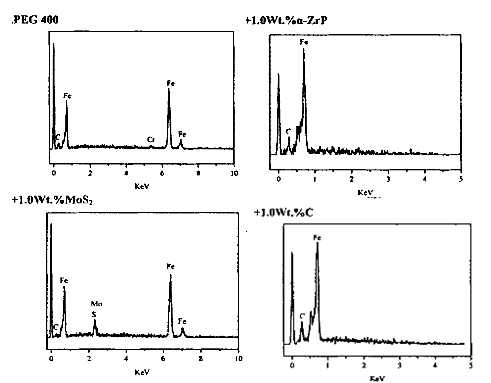
4). EDS Patterns of wear scars lubricated by different additives in PEG400 base oil
Summary
With the development of mechanical equipment,the friction parts often need to work under harsh conditions, such as high temperature, heavy load, strong radiation, low speed, etc. So the conventional lubricating oils can not meet the demand. Solid lubricants can effectively increase the bearing capacity and reduce the friction and wear. Layerde Zirconium Phosphate is a new kind of solid lubricant additive, α-ZrP have showed excellent lubrication ability in the lithium grease and lubricating oils. In order to investigate the tribological properites of α-ZrP in different base oils, α-ZrP as an additive was evaluated with an oscillating reciprocating friction and wear tester. Meanwhile the traditional solid lubricant MoS2 and Graphite were used as references under the same experimental conditions.
Introduction
1. Layered Structure of α-ZrP

2. SEM-images of α-ZrP

3. Scheme of the mechanism for α-ZrP

4. SEM and EDS observation of worn surface of grease with additive of α-ZrP after the test

The testing results about using Zirconium (Hydrogen) Phosphate(ZrP) in solid lubricant
The tribological properites with different additives in PEG 400 Base oil
Firstly, the tribological properties of 1.0wt.% α-ZrP in PEG 400 was investigated under fixed frequency of 5 Hz,applied loads from 100 N to 300 N. The results showed that the dynamic friction coefficient curves were steady, and the average friction coefficients were reduced from 0.129,0.110,0.121 to 0.102,0.087,0.079, respectively. Under the applied load of 200 N and frequency of 1 Hz, the dynamic friction coefficient curve of α-ZrP was no fluctuation.But MoS2,Graphite and base oil PEG 400 failed to complete the test. When the frequency was 10 Hz, the dynamic friction coefficient curve of 1.0wt.% of a-ZrP was also steady, the average friction coefficient of PEG 400 reduced from 0.099 to 0.066. When the load and the frequency were 300 N and 5 Hz, the values of wear volumes (106μm3) were as follows :5.371 of PEG 400, 3.491 of α-ZrP,3.176 of MoS2, and 4.022of Graphite. α-ZrP showed excellent friction-reducing and antiwear (AW) properties in the base oil of PEG 400.
1). Dynamic friction coefficient curves for α-ZrP、MoS2 and Graphite under various applied loads in PEG 400 base oil

Time (min)
(load :100 N/200N/30N;frequency:5 HZ;duration :60min)
(load :100 N/200N/30N;frequency:5 HZ;duration :60min)
2). Friction coefficient for α-ZrP、 MoS2 and Graphite under various frequencies in PEG 400 base oil

Time()min
(load:200N ;frequency:1Hz/5Hz/10Hz;duration :60 min)
(load:200N ;frequency:1Hz/5Hz/10Hz;duration :60 min)
3). SEM Images of wear scars lubricated by different additives in PEG 400 base oil

(load:200 N;frequency:5Hz;duraction:60min)
4). EDS Patterns of wear scars lubricated by different additives in PEG400 base oil

(load:300 N;frequency:5Hz;duraction:60min)
Summary
The SEM micrographs and EDS of the worn surfaces of the steel plates lubricated by α-ZrP were smooth, only a little grooves and gougings, especially under the higher applied load and frequencies, the α-ZrP in base oil PEG400 has a very good anti-abrasion and anti friction effect, α-Zrp particles in the base oil are as the “third body" to protect the friction pair.

Follow WeChat


