Sunshine Factory, Co., Ltd. > Applications > ZrP for Fuel Cell, Lithium BatZrP for Fuel Cell, Lithium Bat
Preparation and Characterization of Proton Exchange Composite Membranes Pore-Filled with ZrP/Sulfonated Polybenzimidazole
SPBI-ZrP/ePTFE proton exchange composite membranes were prepared by pore-filling techniques.
Using ePTFE porous substrate (supporting material) filled with SPBI-ZrP polymer electrolytes.
The microstructure and performance of the membranes were characterized by FESEM, FT-IR, dry-wet weighting method, tensile test and AC impedance.
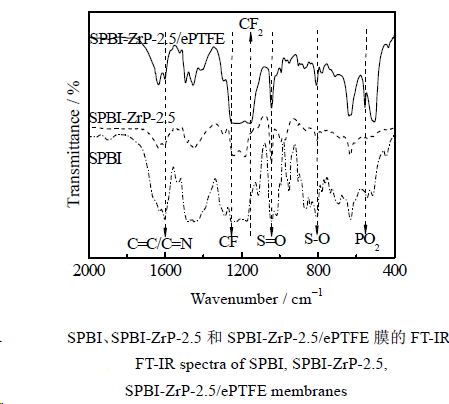
The results indicate that SPBI-ZrP is successfully filled into the ePTFE substrate and the membrane surface is smooth.
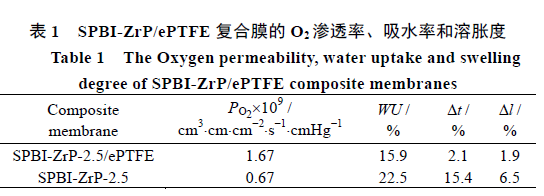
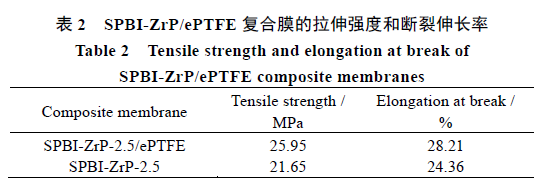
The swelling degree of the SPBI-ZrP-2.5 membrane in thickness direction is about 7.3 times of that of the SPBI-ZrP-2.5/ePTFE membrane, because ePTFE can effectively suppress membrane swelling and improve membrane dimensional stability. Simultaneously, because of the reinforced effect of ePTFE, the mechanical strength of the SPBI-ZrP-2.5/ePTFE membrane is 19.86% higher than that of SPBI-ZrP-2.5.
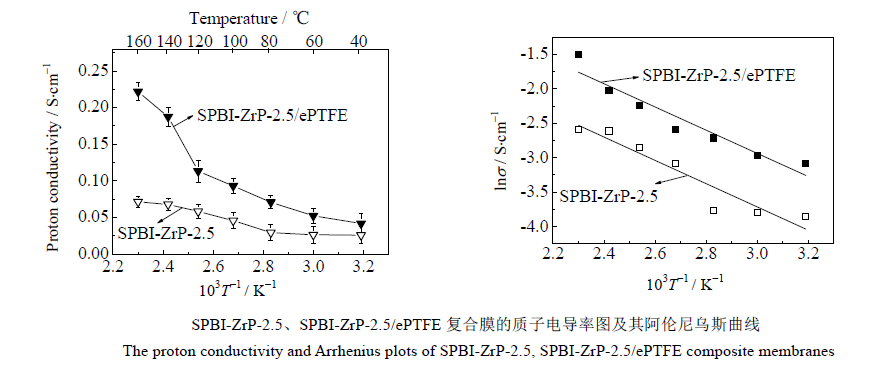
The SPBI-ZrP-2.5/ePTFE membrane shows a high proton conductivity of 0.222 and 0.071 S·cm--1 at 160℃ and 80℃ under 100% relative humidity, respectively. The proton conductivity of Nafion membrane (EW=1100) is 0.077 S·cm-1 at 80℃ and decreases sharply when temperature exceeds 100℃.
These results indicate that SPBI-ZrP/ePTFE membranes have good proton conductivity at higher temperature, which can be applied in fuel cells with high temperature proton exchange membranes.
Results and Discussion

Using ePTFE porous substrate (supporting material) filled with SPBI-ZrP polymer electrolytes.
The microstructure and performance of the membranes were characterized by FESEM, FT-IR, dry-wet weighting method, tensile test and AC impedance.
The results indicate that SPBI-ZrP is successfully filled into the ePTFE substrate and the membrane surface is smooth.
The swelling degree of the SPBI-ZrP-2.5 membrane in thickness direction is about 7.3 times of that of the SPBI-ZrP-2.5/ePTFE membrane, because ePTFE can effectively suppress membrane swelling and improve membrane dimensional stability. Simultaneously, because of the reinforced effect of ePTFE, the mechanical strength of the SPBI-ZrP-2.5/ePTFE membrane is 19.86% higher than that of SPBI-ZrP-2.5.
The SPBI-ZrP-2.5/ePTFE membrane shows a high proton conductivity of 0.222 and 0.071 S·cm--1 at 160℃ and 80℃ under 100% relative humidity, respectively. The proton conductivity of Nafion membrane (EW=1100) is 0.077 S·cm-1 at 80℃ and decreases sharply when temperature exceeds 100℃.
These results indicate that SPBI-ZrP/ePTFE membranes have good proton conductivity at higher temperature, which can be applied in fuel cells with high temperature proton exchange membranes.
Results and Discussion






Follow WeChat


