Sunshine Factory, Co., Ltd. > Applications > ZrP for PolymerZrP for Polymer
Pro-environment flame retardant of polypropylene system with enhanced thermal properties and flame retardancy
Abstract
Layered spherical aggregates of melamine cyanurate complex (MCA) were self-assembled on the surface of α-zirconium phosphate and an inorganic–organic composite flame retardant α-zirconium phosphate@melamine cyanurate(AMC) was synthesized via a facile way.
The influences of AMC on the thermal, mechanical, and flame retardancy of intumescent flame-retardant polypropylene(PP) system were studied.
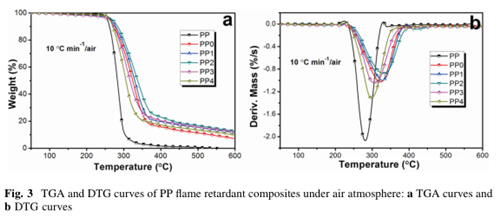
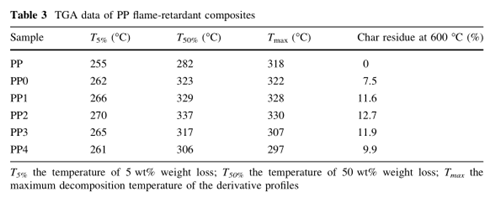
The results indicated that the addition of AMC could enhance the thermal stability of PP composites, and increase the final amount of char residue.
The kinetics studies indicated that more activation energy of degra-dation was necessar when combined with AMC.
Flame-retardant tests revealed that 2 wt% loading of AMC with 24 wt% intumescent flame retardant (IFR) could impart PP composites with the highest values of LOI, reached 31.2%, and passed the UL-94 V-0 rating.
Without the MCA shell, the LOI of PP composites decreased to 27.1% and the V-1 rating was obtained.
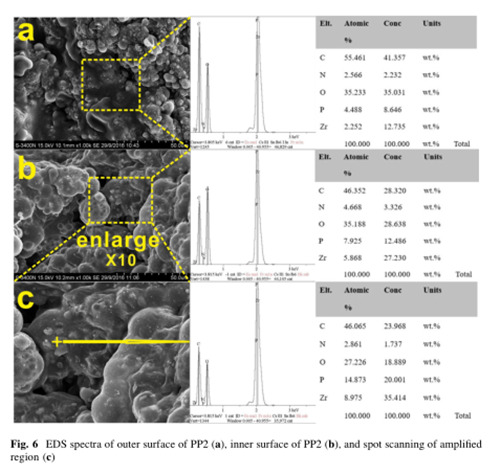
The existence of MCA shell reinforced the synergistic effect between α-ZrP core and IFR.
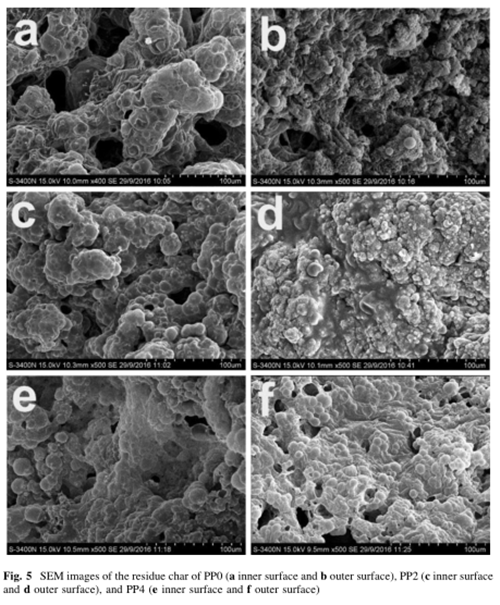
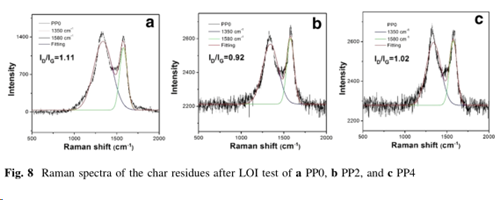
The investigation of char residues indicates that AMC could not only enhance the amount, but also the graphitization of char layer, including physically strengthened effect.
In the end, the mechanical properties were investigated as well.
Experimental
Formulations of PP and PP/AMC composites
Characterization of the as-prepared AMC
Flammability behavior of PP composites

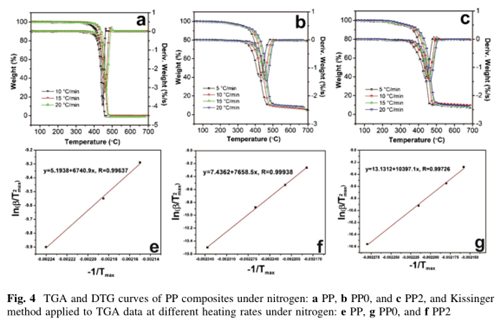
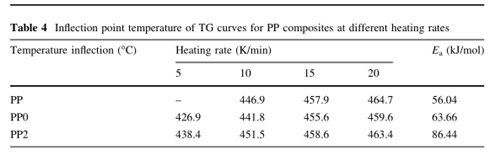
Thermogravimetric analysis
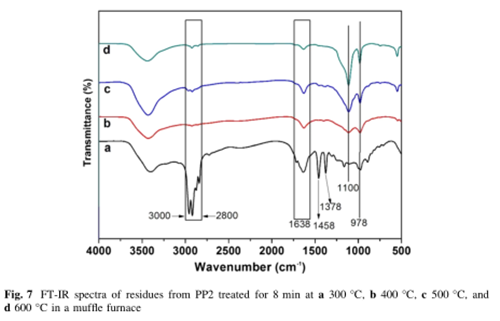
Analysis of char residues
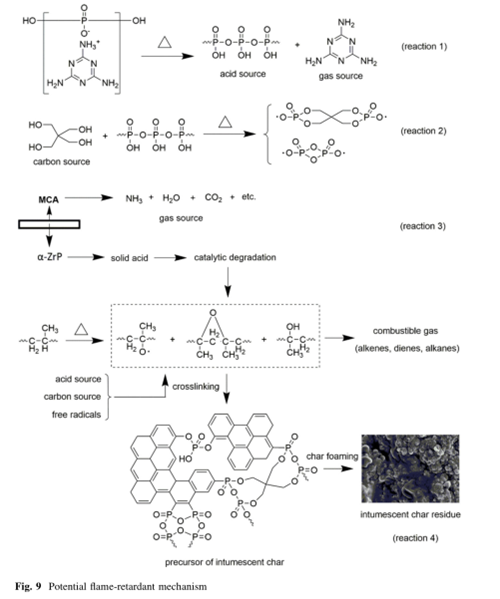
Potential flame-retardant mechanism
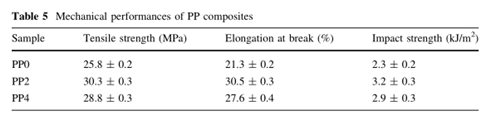
Mechanical properties

Conclusions
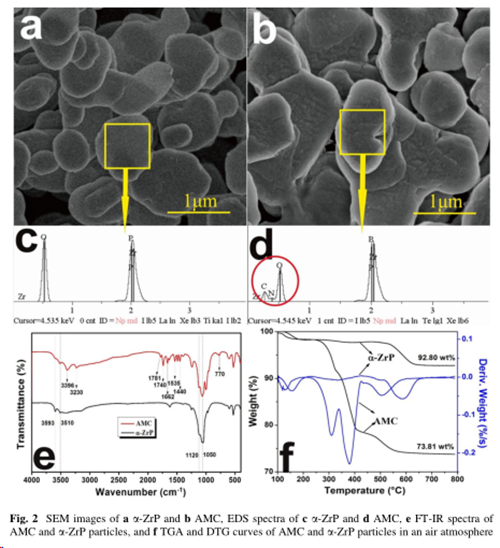
The AMC consists of α-zirconium phosphate and melamine cyanurate.
The synergism between MCA shell and α-ZrP core was found, and α-ZrP core herein was used as one kind of solid acid catalyst, physical barrier, and could display as acid source, not only could accelerate the degradation of PP chain scission, but also could act as the physical barrier to inhibit the mass and heat transferring, and could strengthen the char layer during the combustion to some extent.
MCA shell herein could protect PP chain from contacting with solid acid sites on the surface of α-ZrP core.
Meanwhile, the graphitization of char residue was promoted, indicating that AMC could transfer amorphous char into graphitic structure.
In the end, the mechanical properties were improved with the addition of AMC to some extent, due to the better dispersion and compatibility.
Layered spherical aggregates of melamine cyanurate complex (MCA) were self-assembled on the surface of α-zirconium phosphate and an inorganic–organic composite flame retardant α-zirconium phosphate@melamine cyanurate(AMC) was synthesized via a facile way.
The influences of AMC on the thermal, mechanical, and flame retardancy of intumescent flame-retardant polypropylene(PP) system were studied.
The results indicated that the addition of AMC could enhance the thermal stability of PP composites, and increase the final amount of char residue.
The kinetics studies indicated that more activation energy of degra-dation was necessar when combined with AMC.
Flame-retardant tests revealed that 2 wt% loading of AMC with 24 wt% intumescent flame retardant (IFR) could impart PP composites with the highest values of LOI, reached 31.2%, and passed the UL-94 V-0 rating.
Without the MCA shell, the LOI of PP composites decreased to 27.1% and the V-1 rating was obtained.
The existence of MCA shell reinforced the synergistic effect between α-ZrP core and IFR.
The investigation of char residues indicates that AMC could not only enhance the amount, but also the graphitization of char layer, including physically strengthened effect.
In the end, the mechanical properties were investigated as well.
Experimental
Formulations of PP and PP/AMC composites

Characterization of the as-prepared AMC

Flammability behavior of PP composites

Thermogravimetric analysis


Analysis of char residues





Potential flame-retardant mechanism


Mechanical properties


Conclusions
A planar-like solid acid, α-ZrP, was successfully modified by MCA via self-assembly in a facile way.
The synthesized composite particles AMC were characterized using FESEM, EDS, FT-IR, and TGA.
It was clearly found that theflame retardancy of PP composites could be improved by adding IFR and AMC rather than IFR alone, with an increase in LOI values and the improvement of UL-94 rating.
The highest LOI value of all samples was 31.2% and UL-94 could reach a V-0 rating, while the optimum ratio of IFR to AMC was 12:1.
And the incorporation of AMC led to a significant improvement in thermal stability, not only the T 5% , but also the T 50% and T max were increased, meanwhile, the amount of final char residue was increased as well.
By the investigation of the thermal kinetics of flame-retardant PP system, more activation energy of degradation was necessary.
The synthesized composite particles AMC were characterized using FESEM, EDS, FT-IR, and TGA.
It was clearly found that theflame retardancy of PP composites could be improved by adding IFR and AMC rather than IFR alone, with an increase in LOI values and the improvement of UL-94 rating.
The highest LOI value of all samples was 31.2% and UL-94 could reach a V-0 rating, while the optimum ratio of IFR to AMC was 12:1.
And the incorporation of AMC led to a significant improvement in thermal stability, not only the T 5% , but also the T 50% and T max were increased, meanwhile, the amount of final char residue was increased as well.
By the investigation of the thermal kinetics of flame-retardant PP system, more activation energy of degradation was necessary.
The AMC consists of α-zirconium phosphate and melamine cyanurate.
The synergism between MCA shell and α-ZrP core was found, and α-ZrP core herein was used as one kind of solid acid catalyst, physical barrier, and could display as acid source, not only could accelerate the degradation of PP chain scission, but also could act as the physical barrier to inhibit the mass and heat transferring, and could strengthen the char layer during the combustion to some extent.
MCA shell herein could protect PP chain from contacting with solid acid sites on the surface of α-ZrP core.
Meanwhile, the graphitization of char residue was promoted, indicating that AMC could transfer amorphous char into graphitic structure.
In the end, the mechanical properties were improved with the addition of AMC to some extent, due to the better dispersion and compatibility.
This R&D Published Polym. Bull.DOI 10.1007/s00289-017-2177-x

Follow WeChat


