Sunshine Factory, Co., Ltd. > Applications > ZrP for PolymerZrP for Polymer
A high efficient halogen-free flame retardant PP was proposed.
Realizing the high efficiency of halogen-free flame retardant is one of the biggest challenges and the most urgent issues in the development of high performance polypropylene (PP).
Abtract
Coupling the catalytic carbonization and free-radical quenching mechanism is proposed to be an efficient method to address this issue.
In this work,a functionalized zirconium phosphate (F-ZrP) with good catalytic carbonization capability was synthesized, and was combined with N-alkoxy hindered amine (NOR) to flame-retard PP.
The composition showed high flame-retardant efficiency.
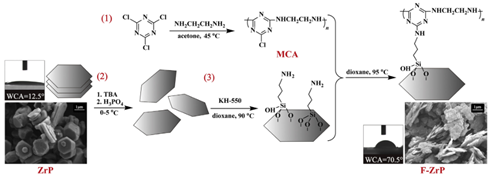
Synthesis of functionalized zirconium phosphate (F-ZrP)
Flame retardancy tests
When the contents of NOR, F-ZrP and APP were 0.2 wt%, 4.95 wt% and 14.85 wt%, respectively, the LOI of PP was increased from 18.0% to 36.0% and the UL-94 rating was increased from NR to V-0 rating.
Besides, the PHRR, AV-HRR, THR, PSPR and TSP were decreased by 95.6%, 90.6%, 73.3%, 93.5% and 80.6%, respectively.
The mechanism revealed that F-ZrP formed closed micron-scale char-cages in intumescent char layer through interfacial carbonization.
In the char cages, the nitroxyl radicals generated by NOR efficiently quenched the active free-radicals produced by the pyrolysis of PP and induced their cyclization reaction.
Synergistic flame-retardant mechanism of NOR and F-ZrP in PP
The synergistic flame-retardant mechanism of NOR and F-ZrP in PP was revealed and shown in Fig.
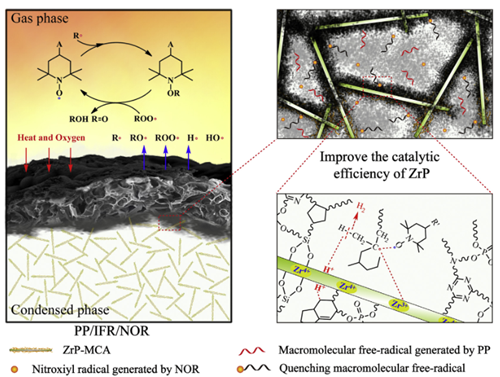

During combustion, the interfacial carbonization of F-ZrP generated lots of sheet chars, which separated the intumescent char layer into countless closed micron-scale char cages.
The nitroxyl radicals generated by NOR and the active free-radicals generated by PP were trapped in the char cages.
Therefore, nitroxyl radicals quenched active freeradicals efficiently and induced them to participate in the cyclization reaction.
The obtained cyclic compounds were captured by the Lewis acid sites (Zr 4+) of ZrP and further catalyzed by the Brønsted acid sites (H+) of ZrP to participate in the carbonization reactions, generating graphitized crystalline char and endowing the char layer with good thermostability and barrier performance.
Meanwhile, nitroxyl radicals also effectively quenched small molecular active free-radicals in the gas phase, weakening the impact of heat and oxygen on the surface of the char layer and extinguishing the fire.
Conclusions
The synergism of N-alkoxy hindered amine (NOR) and functionalized ZrP nanosheet realized the high efficiency of halogen-free flame retardant PP.
The obtained cyclic compounds were captured and catalyzed into graphitized crystalline char by F-ZrP nanosheets, forming stable and compact char layer to protect the polymer from burning.
The synergism of free-radical quenching and catalytic carbonization mechanism provides a new way to realize the high efficient halogen-free flame retardant polymer.
(Contents lists available at ScienceDirect ,College of Materials Science and Engineering, Key Lab of Guangdong Province for High Property and Functional Polymer Materials, South China University of Technology.)

Follow WeChat


