Sunshine Factory, Co., Ltd. > Applications > ZrP for PolymerZrP for Polymer
zirconium phosphate apply in PA Alloy
How effectively improved the tribological performances, mechanical properties and moisture resistance of PA/PPO alloy?
Abstract
A functionalized zirconium phosphate (FZrP) nanosheet was synthesized and introduced to PA46/PPO alloy as a solid lubricant.
FZrP showed a high efficiency in improving the tribological performances, mechanical properties and moisture resistance of PA46/PPO with the incorporation of 2.0% FZrP, the wear loss and friction coefficient of PA/PPO were decreased by 94.48% and 56.60%, respectively.

Moreover, the friction and wear mechanism of FZrP was intensively studied and revealed: FZrP nanosheet retained and accumulated on the wear surface because of its strong interfacial binding force with the matrix, which resulted in the formation of a protective layer with good strength, tenacity and lubricity to resist severe wear damage.
Synthesis of functionalized zirconium phosphate (FZrP) nanosheet
Mechanical properties and hygroscopicity
(A) tensile strength, (B) flexural strength and (C) impact strength of PA/PPO, PA/PPO/ZrP and PA/PPO/FZrP before and after water soaking treatment and
their (D) moisture absorption.

FZrP na-nosheets played a role as barrier to intercept the absorption of moisture.
Therefore, the incorporation of FZrP obviously decreased the hygroscopicity of PA/PPO.
Friction and wear properties
(A) wear loss and (B) friction coefficient of PA46/PPO, PA46/PPO/ZrP and PA46/PPO/FZrP before and after water soaking treatment.

Friction and wear mechanism
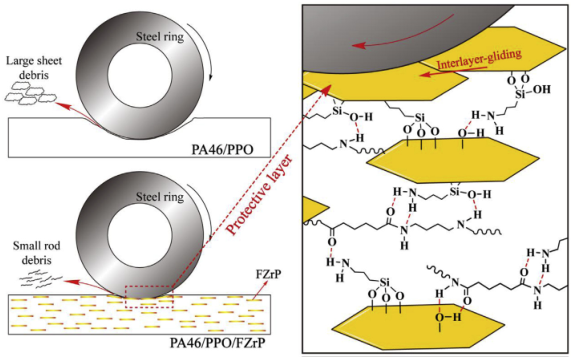
For PA46/PPO/FZrP, every FZrP nanosheet had a large contact area with the PA46/PPO matrix or the other FZrP nanosheets.
Meanwhile, abundant hydrogen bonds were formed between FZrP nanosheets and the PA46 molecular chains.
In this way, every FZrP nanosheet showed a strong interfacial binding force with the PA46/PPO matrix and the other FZrP nanosheets.
Therefore, FZrP nanosheets were difficult to be peeled off and they would retain and accumulate on the wear surface during the wear test, forming a protective layer with good strength and tenacity.
Besides, because of the interlayer-gliding effect of FZrP, the friction coefficient of PA46/PPO/FZrP wear surface was significantly decreased.
Conclusions
A functionalized zirconium phosphate (FZrP) nanosheet was successfully synthesized and it effectively improved the tribological performances, mechanical properties and moisture resistance of PA46/PPO alloy.
With the incorporation of 2.0% FZrP, the wear loss and friction coefficient of PA/PPO were decreased by 94.48% and 56.60%, respectively.
Meanwhile, the tensile strength, flexural strength and impact strength were increased by 15.24%, 9.19% and 36.17%, respectively.
The moisture absorption and the impact of moisture on the mechanical properties and tribological performances were all decreased obviously.
It was revealed that FZrP nanosheets retained and accumulated on the wear surface during the wear test through its strong interfacial binding force with the matrix, forming a protective layer with good strength, tenacity and lubricity.
(Contents lists available at ScienceDirect)
Abstract
A functionalized zirconium phosphate (FZrP) nanosheet was synthesized and introduced to PA46/PPO alloy as a solid lubricant.
FZrP showed a high efficiency in improving the tribological performances, mechanical properties and moisture resistance of PA46/PPO with the incorporation of 2.0% FZrP, the wear loss and friction coefficient of PA/PPO were decreased by 94.48% and 56.60%, respectively.

Moreover, the friction and wear mechanism of FZrP was intensively studied and revealed: FZrP nanosheet retained and accumulated on the wear surface because of its strong interfacial binding force with the matrix, which resulted in the formation of a protective layer with good strength, tenacity and lubricity to resist severe wear damage.
Synthesis of functionalized zirconium phosphate (FZrP) nanosheet
Mechanical properties and hygroscopicity
(A) tensile strength, (B) flexural strength and (C) impact strength of PA/PPO, PA/PPO/ZrP and PA/PPO/FZrP before and after water soaking treatment and
their (D) moisture absorption.

FZrP na-nosheets played a role as barrier to intercept the absorption of moisture.
Therefore, the incorporation of FZrP obviously decreased the hygroscopicity of PA/PPO.
Friction and wear properties
(A) wear loss and (B) friction coefficient of PA46/PPO, PA46/PPO/ZrP and PA46/PPO/FZrP before and after water soaking treatment.

Friction and wear mechanism

For PA46/PPO/FZrP, every FZrP nanosheet had a large contact area with the PA46/PPO matrix or the other FZrP nanosheets.
Meanwhile, abundant hydrogen bonds were formed between FZrP nanosheets and the PA46 molecular chains.
In this way, every FZrP nanosheet showed a strong interfacial binding force with the PA46/PPO matrix and the other FZrP nanosheets.
Therefore, FZrP nanosheets were difficult to be peeled off and they would retain and accumulate on the wear surface during the wear test, forming a protective layer with good strength and tenacity.
Besides, because of the interlayer-gliding effect of FZrP, the friction coefficient of PA46/PPO/FZrP wear surface was significantly decreased.
Conclusions
A functionalized zirconium phosphate (FZrP) nanosheet was successfully synthesized and it effectively improved the tribological performances, mechanical properties and moisture resistance of PA46/PPO alloy.
With the incorporation of 2.0% FZrP, the wear loss and friction coefficient of PA/PPO were decreased by 94.48% and 56.60%, respectively.
Meanwhile, the tensile strength, flexural strength and impact strength were increased by 15.24%, 9.19% and 36.17%, respectively.
The moisture absorption and the impact of moisture on the mechanical properties and tribological performances were all decreased obviously.
It was revealed that FZrP nanosheets retained and accumulated on the wear surface during the wear test through its strong interfacial binding force with the matrix, forming a protective layer with good strength, tenacity and lubricity.
(Contents lists available at ScienceDirect)

Follow WeChat


