Sunshine Factory, Co., Ltd. > Applications > ZrP for PolymerZrP for Polymer
Advances in Flame Retardant Poly(Lactic Acid)
Abstract
Polylactic acid (PLA) has become a commodity polymer with wide applications in a number of fields.
However, its high flammability with the tendency to flow in fire has limited its viability as a perfect replacement for the petrochemically-engineered plastics.
Traditional flame retardants, which may be incorporated into PLA without severely degrading the mechanical properties, are the organo-halogen compounds.
Meanwhile, these compounds tend to bioaccumulate and pose a risk to flora and fauna due to their restricted use. Research into PLA flame retardants has largely focused on organic and inorganic compounds for the past few years.
And, the renewed interest in the development of environmentally sustainable flame retardants (FRs) for PLA has increased significantly in a bid to maintain the integrity of the polymer.
A review on the development of new flame retardants for PLA is presented herein.
Finding
Αlpha-zirconium phosphate (α-ZrP) is an important layered nanostructure material because of its versatile nature and unique anion exchange properties.
It has been widely applied as a FR for several polymers, but its application for PLA is not extensive.
The combined effect of α-ZrP and intumescent flame retardant (IFR) on flame-retardant PLA was investigated .
The result suggests that α-ZrP increases the thermal stability and char yield of PLA .
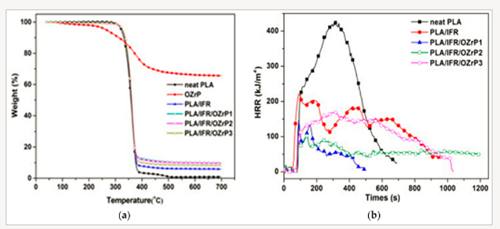
(a) TGA of PLA/IFR/α-ZrP composites; and (b) heat release rate of PLA/IFR/α-ZrP (Adapted with permission from
Interestingly, 1.0 wt % of α-ZrP loading in addition to the intumescent flame retardant led to a 61% reduction in PHRR (Figure b), 81 wt % char residue after the cone calorimeter test, and an increase in LOI to 35.5%.
The FR mechanism of the IFR/α-ZrP was attributed to the flawless compact, smooth, and tight char formed on the surface of the composite which served as a barrier to oxygen and other pyrolysis gases, as shown by the SEM images in below Figure .
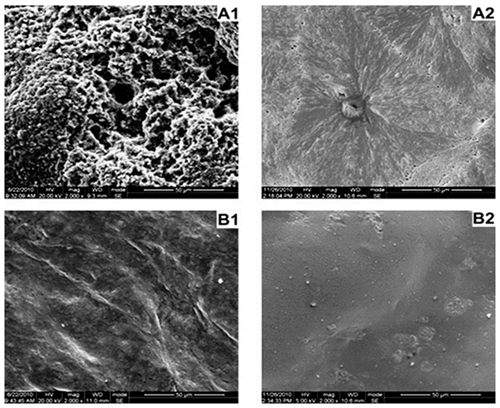
SEM images of char residue after cone calorimeter test: (A1,A2) the outer surface and the inner surface of PLA/IFR; and (B1,B2) the outer and inner surface of PLA/IFR/α-ZrP2
The firm, compact structure of the char obtained from the zirconium-doped PLA/IFR could no doubt resist mass and heat transfer and effectively retard the degradation of the underlying material.
The smooth, homogeneous ceramic-like char obtained was attributed to the perfect balance between α-ZrP and the intumescent FR which protected the material throughout the combustion process and, thus, served as a mechanical reinforcement to the charred layer.
This phenomenon reinforces the conclusion that alpha-zirconium phosphate is an efficient FR additive.
The article from Institute of Textile and Clothing (ITC), The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
However, its high flammability with the tendency to flow in fire has limited its viability as a perfect replacement for the petrochemically-engineered plastics.
Traditional flame retardants, which may be incorporated into PLA without severely degrading the mechanical properties, are the organo-halogen compounds.
Meanwhile, these compounds tend to bioaccumulate and pose a risk to flora and fauna due to their restricted use. Research into PLA flame retardants has largely focused on organic and inorganic compounds for the past few years.
And, the renewed interest in the development of environmentally sustainable flame retardants (FRs) for PLA has increased significantly in a bid to maintain the integrity of the polymer.
A review on the development of new flame retardants for PLA is presented herein.
Finding
Αlpha-zirconium phosphate (α-ZrP) is an important layered nanostructure material because of its versatile nature and unique anion exchange properties.
It has been widely applied as a FR for several polymers, but its application for PLA is not extensive.
The combined effect of α-ZrP and intumescent flame retardant (IFR) on flame-retardant PLA was investigated .
The result suggests that α-ZrP increases the thermal stability and char yield of PLA .

(a) TGA of PLA/IFR/α-ZrP composites; and (b) heat release rate of PLA/IFR/α-ZrP (Adapted with permission from
Interestingly, 1.0 wt % of α-ZrP loading in addition to the intumescent flame retardant led to a 61% reduction in PHRR (Figure b), 81 wt % char residue after the cone calorimeter test, and an increase in LOI to 35.5%.
The FR mechanism of the IFR/α-ZrP was attributed to the flawless compact, smooth, and tight char formed on the surface of the composite which served as a barrier to oxygen and other pyrolysis gases, as shown by the SEM images in below Figure .

SEM images of char residue after cone calorimeter test: (A1,A2) the outer surface and the inner surface of PLA/IFR; and (B1,B2) the outer and inner surface of PLA/IFR/α-ZrP2
The firm, compact structure of the char obtained from the zirconium-doped PLA/IFR could no doubt resist mass and heat transfer and effectively retard the degradation of the underlying material.
The smooth, homogeneous ceramic-like char obtained was attributed to the perfect balance between α-ZrP and the intumescent FR which protected the material throughout the combustion process and, thus, served as a mechanical reinforcement to the charred layer.
This phenomenon reinforces the conclusion that alpha-zirconium phosphate is an efficient FR additive.
The article from Institute of Textile and Clothing (ITC), The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China

Follow WeChat


